Cybersecurity
Point of Sale Security Testing for Enhanced Protection
This Point of View explores the potential vulnerabilities, crucial measure and benefits of performing security testing in the field of Point of Sale (POS) systems. It aims to provide a comprehensive overview of security testing methodologies, best practices and emerging trends to enhance the security integrity of POS systems.
Insights
- This Point of View offers an in-depth look at Point of Sale (POS) systems and the security challenges they face, particularly concerning data security, PCI compliance, and integration vulnerabilities.
- We examined past POS security breaches and emphasized the importance of implementing robust security measures for POS systems.
- Additionally, we explored various security hotspots in retail POS environments and outlined a comprehensive security testing strategy.
Abstract
Point of Sale (POS) systems play a critical role in facilitating transactions for businesses across various industries. POS system, which handle sensitive customer data and business transactions, require robust security measures to prevent data breaches, fraud and unauthorized access. To mitigate the risks associated with POS breaches, it is essential to conduct thorough security testing.
In the current era of escalating cyber threat, this Point of View emphasizes the importance of regular in-depth security testing of POS systems. By highlighting the potential risks and offering mitigation strategies, the study contributes significantly to the ongoing effort to strengthen data security in retail businesses. The results of the testing process will provide insight into the system’s robustness, reliability and readiness against cyber threats, ultimately contributing to enhanced data protection.
Background
Point of sale (POS) refers to the location where a transaction takes place between a merchant and a customer. It typically involves the exchange of goods or services for payment. Traditionally, POS systems consisted of cash registers, barcode scanners, and receipt printers. However, with advancements in technology, modern POS systems have evolved to include digital payment options, inventory management, customer relationship management and more.
The primary purpose of a POS system is to facilitate smooth and efficient transactions for businesses. It allows merchants to record sales, track inventory, generate receipts and manage customer data. It also provides valuable insights into sales patterns, inventory levels, and customer preferences, enabling businesses to make data-driven decisions.
Since POS systems manage sensitive customer data, including payment card details, they also become attractive targets for cybercriminals. Data breaches and security vulnerabilities in POS systems can result in the compromise of customer data, financial losses and reputational damage for businesses.
Here are some notable examples of POS security breaches:
- DoorDash: A breach that occurred in May 2019 impacted 4.9 million customers, delivery workers, and merchants who had created accounts before April 5, 2018. Hackers stole information including names, email and delivery addresses, order history, phone numbers, and passwords.
- Wawa: POS malware was planted in the systems of over 800 Wawa convenience stores and went undetected for 8 months. This malware reportedly harvested payment information, including names, card numbers, and expiration dates.
To mitigate such risks, businesses need to implement robust security measures for their POS systems. This includes regular security testing, which involves evaluating the system's vulnerabilities, identifying potential weaknesses, and implementing essential safeguards to make sure the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of customer data.
Challenges in POS Security
- Data Security: POS system handle sensitive customer data, thereby making data protection a primary concern.
- Payment Card Industry (PCI) Compliance: Retailers must ensure their POS systems are compliant with PCI standards.
- Integration with Other Systems: The integration of POS systems with other system can introduce additional security vulnerabilities.
POS Security Testing Strategy
A robust point of sale security testing strategy should include the following steps.
Figure 1: POS security testing process flow
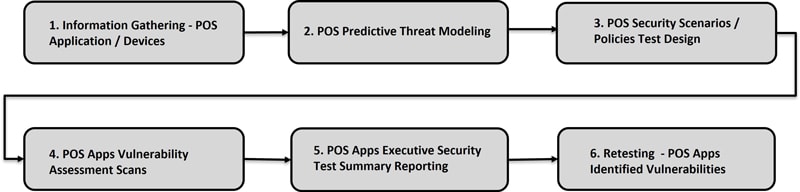
1. POS Information gathering: Security Analyst begin by gaining a comprehensive understanding of the POS system’s architecture, components, and functionalities. This will help in identifying potential weak point or misconfigurations that could be exploited by the attackers. Testers can assess a POS system’s security by gathering information about its operating system, web server, programming language, database and framework. This allows a security analyst to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the POS system’s hardware and software components. The hardware typically includes a computer, table, barcode scanner, and printer, while the software handles transactions, inventory, payment processing, and reports.
2. POS Predictive Threat model: Threat modelling is a proactive approach to identify, understand, and manage potential threats that can compromise the security of a system. It allows the team to identify and categorize potential threats, which can then be prioritized based on their severity. For example, if a threat model identifies POS system is vulnerable to SQL injection attack, then team can work on fixing the vulnerability even before it is exploited. Thus, helping the team to allocate their resources effectively by focusing on the most significant threats. Team can perform threat modeling on their POS system once a year to ensure their systems are secure against the latest threats.
Here is a brief and limited checklist, which is not exhaustive, for identifying specific countermeasures for potential threats.
STRIDE Threats / Mitigation Strategies for Point-of-Sale Apps
| Type of threat | Techniques for Mitigation |
|---|---|
| Spoofing Identity | Ensure Secure authentication in POS system by
|
| Tampering with data | Ensure POS system data are Tamper proof by applying
|
| Repudiation | Ensure POS system is non-repudiation by applying
|
| Information Disclosure | Ensure POS system is not revealing any sensitive information by applying proper
|
| Denial of Service | Make sure POS systems are not vulnerable to denial of service by applying
|
| Elevation of privilege |
|
3. Security Test Design: Used for Identifying abuse scenarios and mapping policies to the POS apps/systems. The test design should be comprehensive, covering all components of the POS systems such as hardware, software, network connections and user access control for thin and thick client.
4. Vulnerability Assessment: Security tester can leverage automated tool to scan the POS systems for known vulnerabilities followed by manual testing. Automated commercial scanners provide a comprehensive scan of the system and generate a report of potential vulnerabilities. However, commercial security tools are not accurate in results and can sometimes generate false positive. False positive can occur due to various reasons, such as outdated vulnerability database, misconfiguration, or limitations in the scanning tool itself. Automated security scans usually work on configurations based on general rules. Hence, by performing manual security testing, a wide range of POS apps testing scenarios can be covered that are missed during automation scans.
There are industry tools such as Burp Suite, Nessus, NMAP etc. that can be extensively used to do the vulnerability assessment scans. The vulnerability assessment using these tools provides information on below:
- Detecting security vulnerabilities such as cross-site scripting and SQL injection in POS applications and APIs through both manual and automated testing techniques.
- Identifying vulnerabilities by performing comprehensive scans on operating systems, cloud services, and other network resources. Remote scanning can alert you to any vulnerabilities that malicious hackers might exploit to gain access to any computer connected to your network.
- Identifying vulnerabilities on IP addresses and open ports within a network, as well as detecting installed applications. This enables network administrators to discover which devices are running on their network, find open ports and services, and detect vulnerabilities.
5. Reporting: Security team, post assessment of the system will generate a detailed executive summary report outlining the observed POS apps vulnerabilities, their associated risks, and recommend right mitigation strategies for identified POS threats. The report should be shared with relevant stakeholders, such as IT management, security teams, and system owners, to ensure that identified vulnerabilities are addressed and the necessary security measures are implemented.
6. Retesting: Depending on the level of risk, developer should prioritize and fix the POS identified vulnerabilities. Once vulnerabilities have been addressed, team should conduct a verification test to ensure that the fixes have been effective in POS apps/systems.
POS Security Testing Hotspots
POS security testing typically involves various techniques, such as Secure configuration, vulnerability assessments and network scanning. These tests help identify potential entry points for attackers, weaknesses in the system's configuration, and any vulnerabilities that could be exploited.
Point of sale security testing hotspot mapping helps in identifying and visualizing potential vulnerabilities in a POS system. In this process, a variety of penetration tests, configuration review, vulnerability assessments and security auditing methods are used to uncover areas within the system that are most susceptible to attacks.
Figure 2: POS Connectivity and Security Hotspots
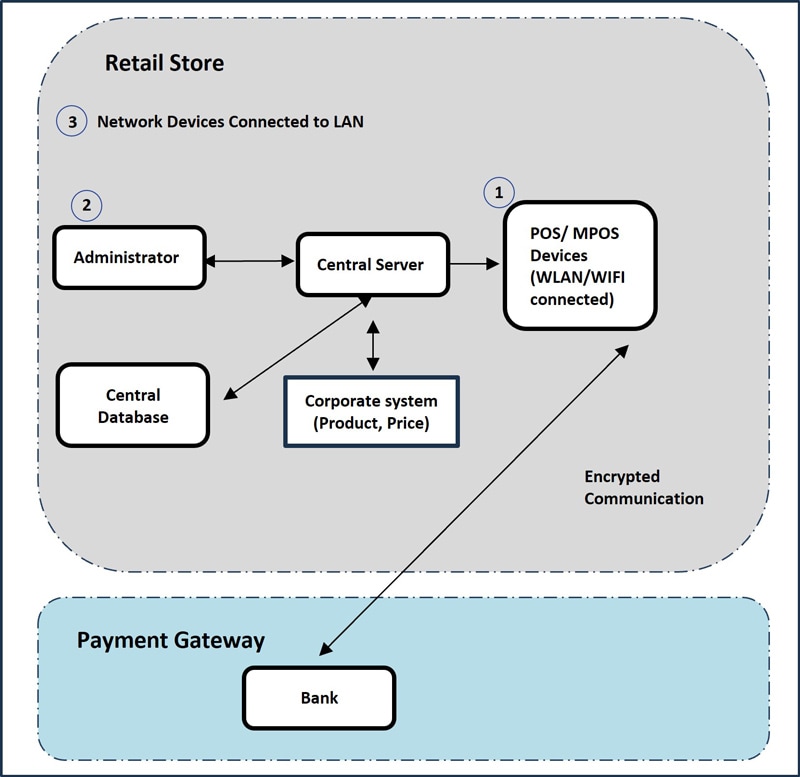
1. POS and MPOS Application security testing (Thin/Thick Client)
POS and MPOS devices connected to Wi-Fi must undergo thorough security testing to ensure that the applications they use are safe and secure from any potential threats or breaches, thereby protecting both the business and its customer.
Application security testing is a process used to identify, rectify, and prevent potential vulnerabilities or security flaws in a software application. The goal is to ensure the application is safe from threats and attacks that may lead to data breaches, loss of information or other significant damages.
Dynamic application security testing involves inspecting an application during its running state. It is designed to find security vulnerabilities that can be exploited while the application is active.
These include security issues such as
- OWASP Top 10: Validate list of topmost critical security risks in web applications. It includes Injection, Broken authentication, Injection, Broken Access control, Cross site scripting, Insufficient logging and Monitoring.
- Privilege escalation: Unauthorized user or a malicious program gains elevated access to resources.
- Data Manipulation: Uncover vulnerabilities in a system that could allow unauthorized alteration of data.
- PIN Validation: Testing with invalid or no PIN for the transaction during product purchase.
- Sensitive Data exposure: Unauthorized or unintended disclosure of sensitive or confidential information of user’s PII information such as account number, card details, social security number or personal address on transaction receipt or exposed anywhere in the system.
2. Secure Configuration review of POS systems
Secure Configuration review is designed to ensure that the POS system is properly configured and secured against potential threats. It involves evaluating the system’s security settings, software, hardware and network configuration.
It includes configuration review such as
- Password Policy: Ensure that strong and unique passwords are being used and changed regularly.
- Default Credential: Ensure that all default credentials are changed, and strong password policies are enforced.
- Network connectivity of POS: Ensure POS network is segregated, and no other user should be able to access the same network.
- Encryption configuration: Ensure encryption setting available on the POS is enabled and properly configured.
- Insecure Data Storage: Ensure configuration file for encrypted data storage is enabled. It is used to secure sensitive information, including personal data, card details, and other confidential data at rest.
- Logs: Ensure device logs are enabled to track any suspicious activities.
3. Vulnerability Assessment – Network devices connected to LAN
This process involves the use of manual and automated network security scanning tool such Nmap, Nessus to run series of network scan to identify weaknesses that could be exploited. It includes analyzing the network for weak configurations, outdated software with known vulnerabilities, improper system settings and other potential risk that could lead to a security breach. It involves technique such as port scanning, network mapping, and other methods of gathering information.
It includes assessment such as:
- Operating System fingerprinting: The process of identifying the operating system type and version to exploit the known security vulnerabilities.
- Port Scan: Limited ports which are absolutely needed for the end point should be enabled without giving out much information.
- Service Scan: Services running on the ports has to give out limited to low information.
- Device Enumeration: Validate all remote connected devices (printer, router etc.) not revealing any sensitive information.
- POS Application Version Vulnerability: It refers to weakness or flaws present in a specific version of a software application. With an outdated or unpatched application an attacker can exploit the known vulnerabilities associated with the application.
Benefits of security testing for point-of-sale system
- Vulnerability identification: Security testing of a point of sale (POS) system helps identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the system's architecture, software, and hardware components. This enables businesses to proactively address potential security risks before they can be exploited by attackers.
- Protection against data breaches: POS systems manage sensitive customer information, such as credit card details and personal data. Security testing ensures the system is well-protected against data breaches, minimizing the risk of financial loss, reputational harm, and legal issues.
- Adherence to industry regulations: Many industries, such as retail and hospitality, have specific regulations and standards related to data security and privacy. By conducting security testing on their POS systems, businesses can ensure compliance with these regulations, avoiding penalties and maintaining customer trust.
- Prevention of unauthorized access: Security testing helps identify potential vulnerabilities that could allow unauthorized users to gain access to the POS system. By strengthening access controls and implementing proper authentication mechanisms, businesses can reduce the risk of unauthorized access and unauthorized transactions.
- Protection against malware and ransomware: Security testing can help identify vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malware or ransomware attacks. By ensuring that the POS system is secure against these types of threats, businesses can prevent downtime, loss of data, and financial loss. This helps protect customer payment information and prevents fraudulent transactions.
- Incident response readiness: Security testing can simulate various attack scenarios, helping businesses assess their incident response capabilities. This includes evaluating the effectiveness of security controls, incident detection mechanisms, and incident response plans. By identifying any gaps and weaknesses, businesses can improve their readiness to respond to security incidents effectively.
- Continuous improvement: Security testing is not a one-time activity but an ongoing process. By regularly conducting security tests and assessments on their POS systems, businesses can continuously improve their security posture, adapting to new threats and vulnerabilities as they arise.
Conclusion
The threat landscape for POS system is constantly evolving, making regular security testing crucial for all retailers. Proper testing of your POS systems plays a vital role so that business can safeguard it from potential threats, protect their customer data, maintain a robust and secure retail environment by following best practices, implementing security measures, and using the right tools and frameworks.
Infosys Quality Engineering services provide best-in-class talents, tools and frameworks for a seamless and secure transition to POS security testing.
References
During the planning of this Point of View, we gathered knowledge and understanding from various credible sources, such as research papers, artifacts. The primary sources that contributed to the development of this Point of View include:
These references formed the basis for the conversations, visions, and suggestions presented in this Point of View.

Subscribe
To keep yourself updated on the latest technology and industry trends subscribe to the Infosys Knowledge Institute's publications
Count me in!









